Seznamy 100 Atom Economy Zdarma
Seznamy 100 Atom Economy Zdarma. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are …
Tady An Introduction To Atom Economy Knockhardy Publishing 2015 Specifications Ppt Download
% atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.% atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:
The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.

Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\). % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100... Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. . The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are …. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are... % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

% atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:.. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.
Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100... Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.

Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100... Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are …. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.

Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. . Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are …

The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100... Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are …

% atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: . % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.

Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.

The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are... % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.

Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\). % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.
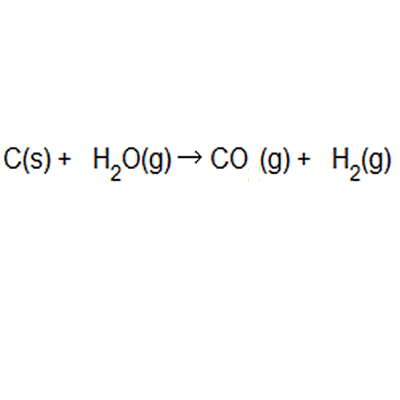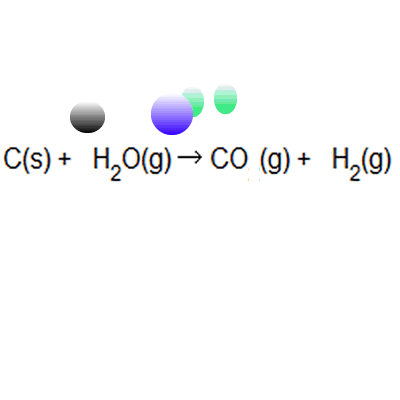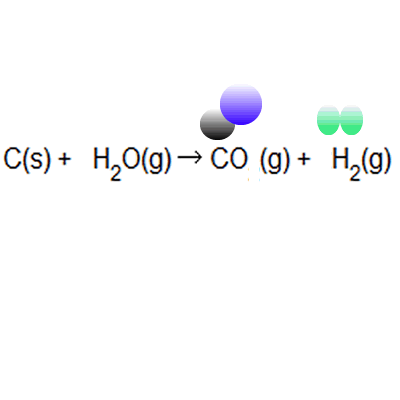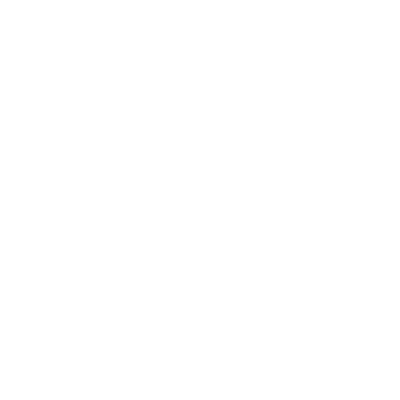
Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.

Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\).. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are ….. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.

The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.

% atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:.. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.

The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.

The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.

Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)
Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.

Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

% atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.

The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.

% atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are …. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are ….. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

% atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.

Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

% atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.

The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\).. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.

The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. . % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.
The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. .. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule... % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.
The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are …

% atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are …. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\). Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

% atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are …

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100... Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.

Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\).. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.

Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\).. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.

% atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100.

Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100... % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are …

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.

The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100... Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are …

Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. .. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.

% atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are ….. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.

Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are …

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.. Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.

% atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule.

% atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100.

Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100... Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100... Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\)

Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\). Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\) % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:. % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products:

Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … Atom economy = \ (\frac {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of the desired product}} {\textup {total m}_ {r} \textup {of all reactants}}\) × 100. % atom economy = (fw of atoms utilized/fw of all reactants) x 100 = (137 /137) x 100 = 100% atom economy in rearrangement reactions rearrangement reactions involve reorganization of the atoms of a molecule. Because neither elimination, addition or substitution of atoms is taking place, in the molecule undergoing rearrangement, the atom economy of rearrangement reactions is 100% and they are … % atom economy = mass of desired product mass of desired product + mass of waste products: The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are. Atom economy = \(\frac{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of the desired product}}{\textup{total m}_{r} \textup{ \\ of all reactants}}\) × 100. Atom economy = \(\frac{6}{34} \times 100\). The atom economy of a reaction is 100% if there are.